Nearly 700,000 children are victims of neglect in the United States each year, according to the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. This staggering number underscores a harsh reality: child neglect is a pervasive issue that demands attention. Child neglect crime refers to the failure of a parent or caregiver to provide for a child’s basic needs, including food, shelter, education, and medical care. It is a serious offense with profound consequences for a child’s physical and emotional well-being.
Understanding what constitutes child neglect crime is crucial for parents, caregivers, and society at large. It is not merely about occasional oversight but a persistent pattern of behavior that harms a child’s development. Recognizing the different types of neglect empowers individuals to identify warning signs, intervene appropriately, and prevent long-term damage. This knowledge is not just for professionals working with children; it is for anyone who cares about the safety and well-being of the next generation.
Understanding Child Neglect Basics
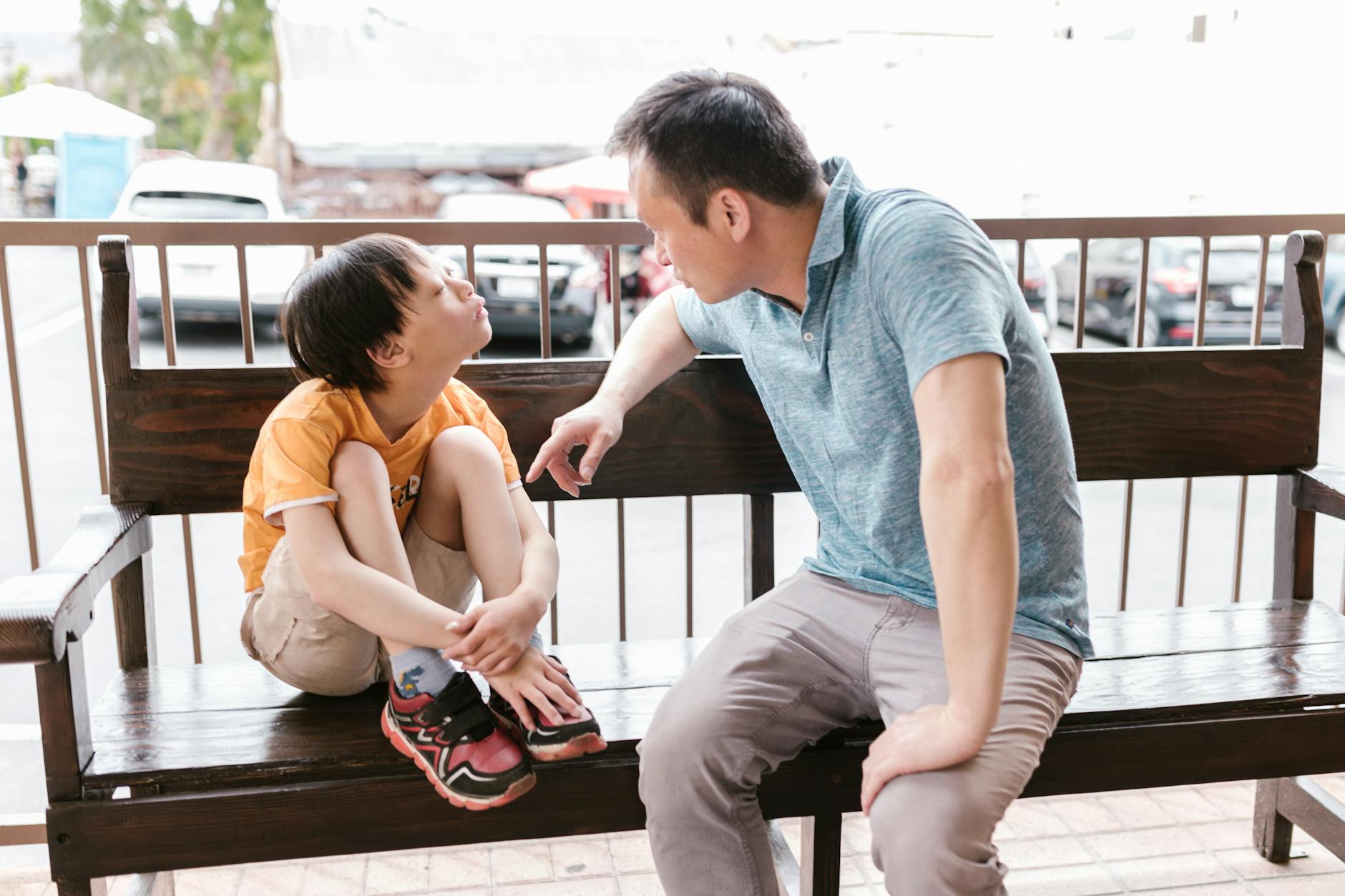

Child neglect is a serious crime that involves failing to provide for a child’s basic needs, potentially causing harm or putting the child at risk. This form of abuse isn’t always obvious, as it often involves a lack of action rather than overt violence. Neglect can be physical, emotional, educational, or medical, and it can have long-lasting effects on a child’s development and well-being.
According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, nearly 61% of all child abuse cases involve neglect. It’s crucial to recognize that neglect isn’t always intentional. Sometimes, parents or caregivers may struggle with their own issues, such as mental health problems or substance abuse, which can hinder their ability to care for their children adequately.
Child neglect can manifest in various ways. Physically, it might involve failing to provide adequate food, clothing, or shelter. Emotionally, it could mean not offering love, support, or guidance. Educational neglect might involve not enrolling a child in school or ensuring they attend regularly. Medical neglect occurs when a caregiver doesn’t provide necessary healthcare or follow through with medical treatments.
Experts emphasize that understanding the signs of neglect is the first step in prevention. Teachers, healthcare providers, and other professionals who work with children are often trained to spot these signs. However, anyone can play a role in protecting children by being aware and reporting suspicions to the appropriate authorities.
Recognizing Emotional Neglect Signs

Emotional neglect, often overlooked, can have profound effects on a child’s development. It manifests in various ways, such as dismissing a child’s feelings, failing to provide love and support, or consistently ignoring their emotional needs. Children experiencing emotional neglect may exhibit signs like low self-esteem, difficulty forming relationships, or a lack of empathy. These signs can be subtle, making them harder to recognize than physical neglect.
According to a study by the American Academy of Pediatrics, emotional neglect can be as damaging as physical abuse. It can lead to long-term mental health issues, including depression and anxiety. Parents might not realize their actions—or lack thereof—are causing harm. They may believe they are protecting their children from emotional pain by avoiding difficult conversations or dismissing their feelings.
Experts emphasize the importance of open communication and active listening. Parents should create a safe space for their children to express their emotions. This involves validating their feelings, offering comfort, and providing guidance. Simple actions, like asking about their day or showing interest in their activities, can make a significant difference. Recognizing the signs of emotional neglect is the first step toward addressing it.
Physical Neglect: What to Watch For

Physical neglect is one of the most common forms of child neglect, yet it often goes unnoticed. It occurs when a caregiver fails to provide for a child’s basic physical needs, such as food, clothing, shelter, or medical care. This type of neglect can have severe consequences on a child’s health and development. According to the Childhelp National Child Abuse Hotline, physical neglect accounts for approximately 80% of all child abuse cases in the United States.
Parents and caregivers should watch for signs such as consistent hunger, poor hygiene, or inappropriate clothing for the weather. Children who are frequently absent from school or who have untreated medical or dental issues may also be victims of physical neglect. Behavioral changes, such as withdrawal, aggression, or age-inappropriate behavior, can also indicate neglect.
Experts emphasize that physical neglect is not always intentional. It can result from a caregiver’s lack of knowledge, mental health issues, or overwhelming life circumstances. However, the impact on the child remains the same, regardless of the caregiver’s intent. Recognizing the signs early can prevent long-term harm and ensure the child receives the necessary support and care.
If physical neglect is suspected, it is crucial to report it to local child protective services or a trusted professional, such as a teacher or healthcare provider. Early intervention can make a significant difference in a child’s life, providing them with the opportunity to thrive in a safe and nurturing environment.
Educational Neglect and Its Consequences

Educational neglect stands as one of the most damaging forms of child neglect, with profound consequences that echo throughout a child’s life. This type of neglect occurs when parents or caregivers fail to provide adequate educational opportunities, whether through enrollment in school, support for learning, or addressing learning disabilities. The result is a child left behind, struggling to keep pace with peers and facing long-term academic and social challenges.
According to a study by the National Center for Education Statistics, children who experience educational neglect are significantly more likely to drop out of school. This statistic underscores the critical role education plays in a child’s development and future prospects. Without proper education, children are at a higher risk of poverty, unemployment, and involvement in criminal activities.
Experts emphasize that educational neglect doesn’t always mean a child is unenrolled from school. It can also manifest as a lack of engagement or support from parents. For instance, a child might attend school but receive no help with homework, no encouragement to read, or no assistance in developing essential study skills. This passive form of neglect can be just as harmful as outright refusal to enroll a child in school.
The consequences of educational neglect extend beyond academic performance. Children who are educationally neglected often struggle with low self-esteem, behavioral issues, and difficulty forming healthy relationships. These challenges can persist into adulthood, creating a cycle of neglect and disadvantage that is difficult to break. Recognizing and addressing educational neglect early is crucial for breaking this cycle and giving children the opportunities they deserve.
Preventing Neglect Through Awareness

Child neglect remains one of the most pervasive forms of abuse, often going unnoticed due to its subtle nature. According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, nearly 61% of all child abuse cases involve neglect. Parents and caregivers must recognize the signs to prevent long-term harm to children’s physical and emotional well-being.
Awareness campaigns play a crucial role in educating communities about the various forms of neglect, including physical, educational, emotional, and medical neglect. Experts emphasize that understanding these categories helps caregivers identify potential issues early. Simple actions, such as ensuring a child attends school regularly or receives proper medical care, can make a significant difference.
Parents should also be mindful of their own behaviors. Neglect can sometimes stem from stress, lack of knowledge, or overwhelming circumstances. Seeking support from family, friends, or professional services can prevent situations from escalating. Early intervention programs and parenting classes provide valuable resources for those struggling to meet their children’s needs.
Schools and healthcare providers are often the first to notice signs of neglect. Teachers and doctors are trained to identify patterns that may indicate a child is not receiving adequate care. Reporting concerns to child protective services can initiate the help a family needs. Communities that foster open communication and support systems create a safer environment for all children.
Child neglect is a serious issue that can have lasting impacts on a child’s development and well-being. Recognizing the four types—educational, emotional, physical, and medical—is the first step in prevention and intervention. Parents and caregivers should stay informed, maintain open communication with children, and seek help when needed, as early intervention can make a significant difference. Moving forward, increased awareness and support systems can help ensure every child grows up in a safe and nurturing environment.