Every year, thousands of criminal cases hinge on the proper handling of evidence. A single mishandled piece can lead to wrongful convictions or criminals walking free. Police evidence handling is the meticulous process of collecting, preserving, and managing physical and digital evidence to maintain its integrity throughout the criminal justice process. It serves as the backbone of any investigation, ensuring that evidence remains admissible in court and reliable for prosecution.
Understanding what is police evidence handling is crucial for anyone interested in law enforcement or criminal justice. It involves a series of standardized procedures designed to prevent contamination, loss, or tampering. From the moment evidence is collected at a crime scene to its presentation in court, every step must adhere to strict protocols. Proper police evidence handling not only upholds the legal standards but also ensures justice is served accurately and fairly.
Understanding Evidence Handling Basics
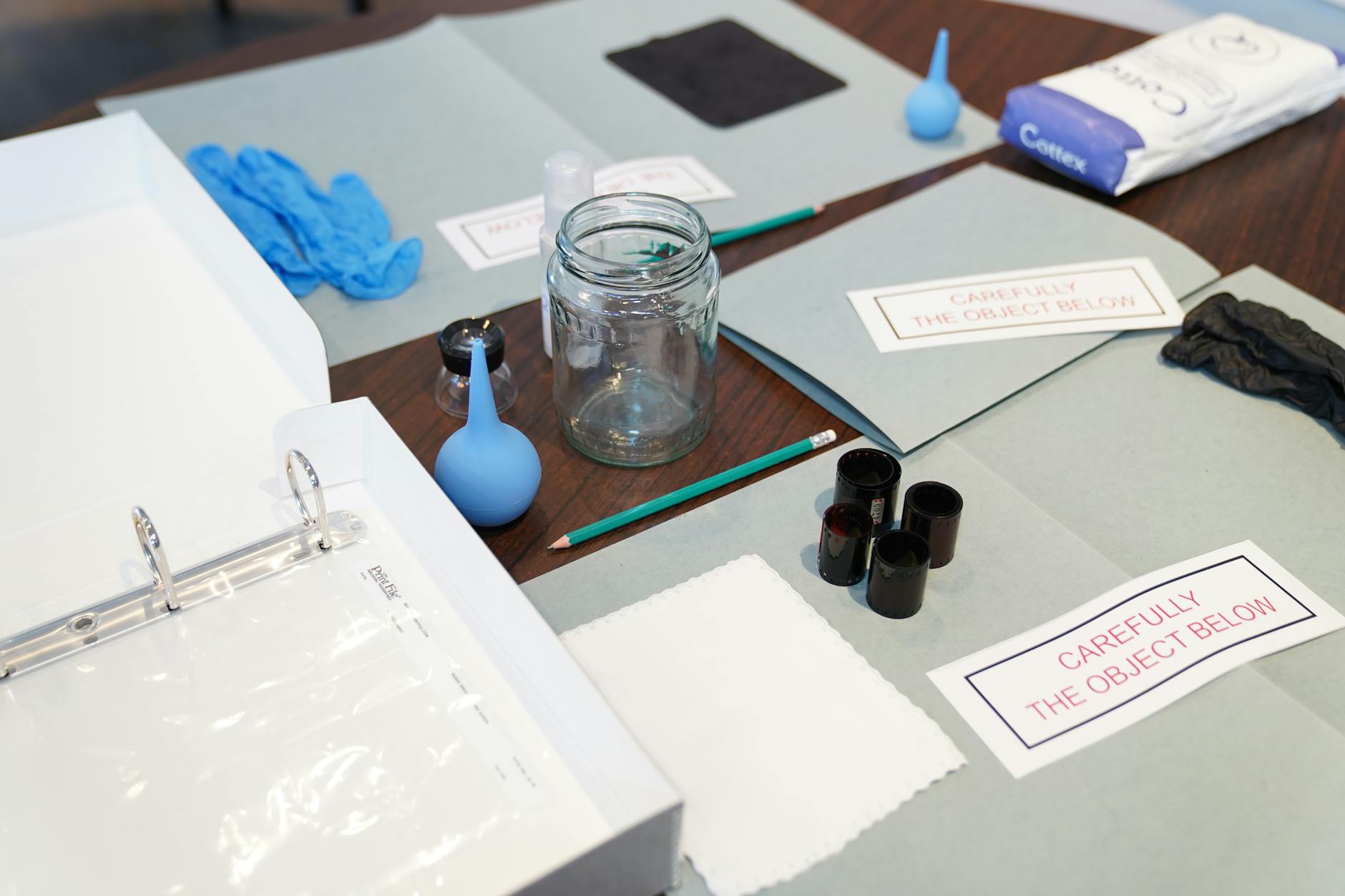

Police evidence handling forms the backbone of any criminal investigation. It encompasses the collection, preservation, and analysis of physical and digital evidence that can make or break a case. Proper handling ensures the integrity of evidence, maintaining its admissibility in court. According to the National Institute of Justice, mishandled evidence can lead to wrongful convictions or acquittals of guilty parties.
Evidence can take many forms, including biological materials, weapons, digital data, and documents. Each type requires specific handling procedures to prevent contamination or degradation. For instance, biological evidence must be collected using sterile tools and stored at controlled temperatures. Digital evidence, on the other hand, needs to be imaged and analyzed using specialized software to avoid data corruption.
Police officers and crime scene investigators undergo rigorous training to master evidence handling techniques. They learn to document the chain of custody meticulously, ensuring that every transfer of evidence is recorded. This chain is crucial for proving that evidence has not been tampered with or altered in any way. A break in the chain can render evidence inadmissible, undermining the entire investigation.
Understanding these basics is the first step in proper police evidence handling. It sets the stage for the subsequent steps, which include securing the scene, collecting evidence, preserving it, analyzing it, and presenting it in court. Each step builds upon the previous one, creating a robust framework for justice. Experts emphasize that consistency and attention to detail are key to successful evidence handling.
Critical Components of Proper Collection
Proper police evidence handling begins with critical components that ensure the integrity and admissibility of evidence in court. Chain of custody stands as the cornerstone, meticulously documenting every transfer of evidence from collection to presentation. This unbroken trail prevents tampering and contamination, with studies showing that 90% of evidence challenges in court stem from chain of custody breaches.
Evidence collection requires specialized tools and techniques tailored to the type of evidence. For biological samples, sterile containers and swabs prevent degradation, while digital evidence demands forensic imaging to preserve data integrity. Officers must receive ongoing training to adapt to evolving technologies and methodologies.
Documentation plays a pivotal role in evidence handling. Detailed notes, photographs, and diagrams create a comprehensive record of the scene and evidence condition. The National Institute of Justice emphasizes that thorough documentation reduces disputes and strengthens prosecutions.
Proper packaging and labeling ensure evidence remains uncontaminated and identifiable. Each item receives a unique identifier, and packaging materials prevent degradation. For example, paper bags breathe to preserve biological evidence, while metal containers shield electronic devices from electromagnetic interference.
Chain of Custody Explained

Police evidence handling involves a critical process known as the chain of custody. This meticulous documentation tracks every individual who handles evidence from its collection to its presentation in court. Proper chain of custody ensures evidence remains uncontaminated and its integrity preserved. Without this documentation, evidence may be deemed inadmissible in court.
Each time evidence changes hands, the responsible party must record their name, title, and the date and time of transfer. This creates an unbroken chain that demonstrates the evidence has not been tampered with. According to the National Institute of Justice, maintaining a proper chain of custody is crucial for the admissibility of evidence in criminal proceedings.
Breaches in the chain of custody can occur due to improper handling, inadequate documentation, or lack of supervision. Even minor lapses can compromise evidence, potentially leading to wrongful convictions or acquittals. Police officers and forensic specialists must adhere to strict protocols to prevent such occurrences.
Best Practices for Secure Storage
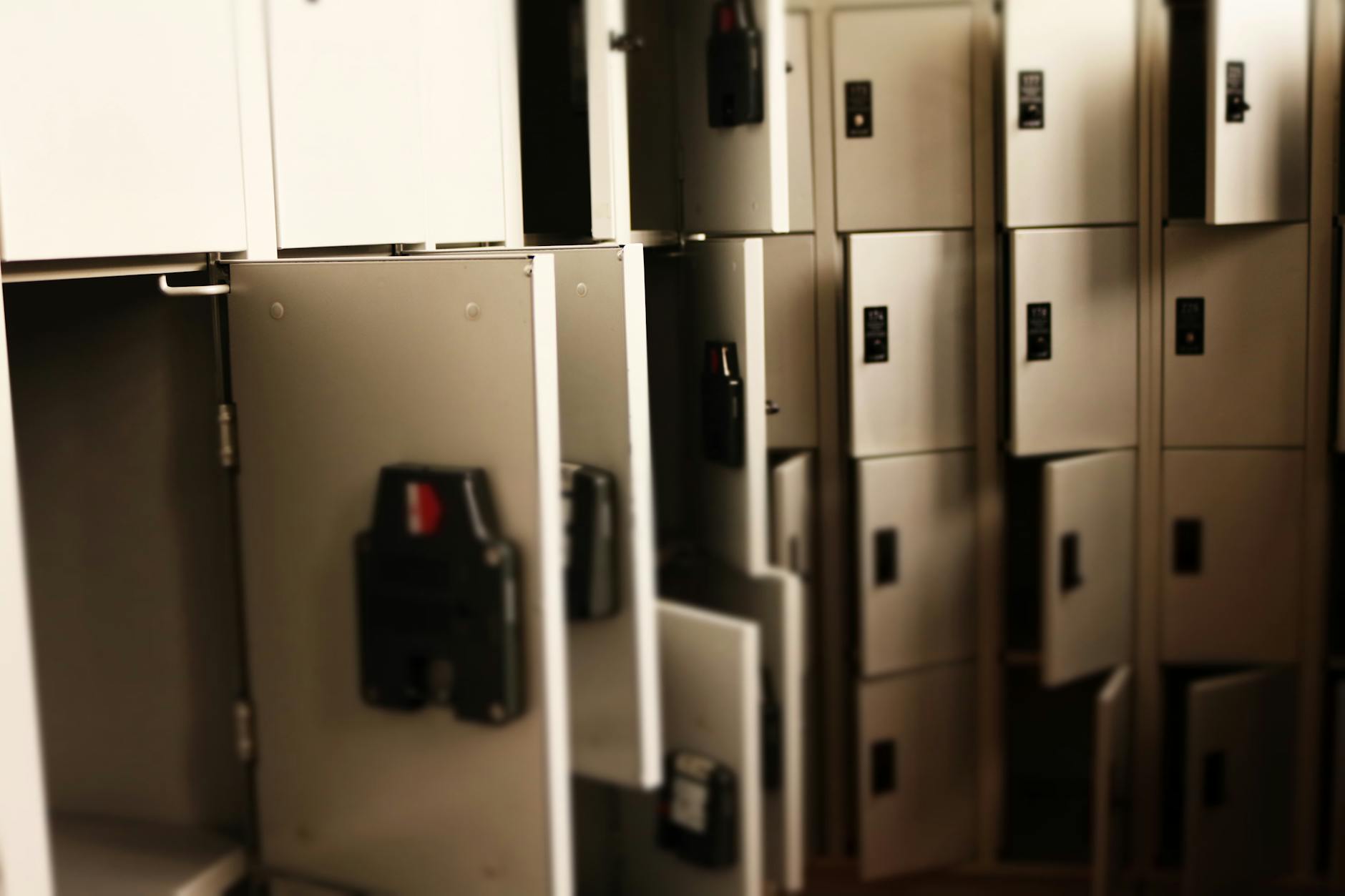

Secure storage forms the backbone of effective police evidence handling. Every piece of evidence, from physical objects to digital data, requires meticulous care to maintain its integrity. Officers must follow strict protocols to prevent contamination, loss, or tampering. Chain of custody documentation plays a crucial role here, ensuring every transfer of evidence is properly recorded.
Experts recommend using tamper-evident packaging for physical evidence. These specialized containers show clear signs if someone attempts to open them without authorization. For digital evidence, secure storage involves encrypted drives and password-protected systems. According to a recent study, proper storage techniques can reduce evidence contamination by up to 40%.
Temperature and environmental controls are essential for certain types of evidence. Biological samples, for instance, require specific conditions to remain viable. Officers should consult with forensic specialists to determine the appropriate storage parameters. Regular audits of storage facilities help maintain these standards and identify potential issues early.
Digital evidence presents unique challenges that require specialized approaches. Cloud storage solutions with robust security measures can protect sensitive data. Officers must also ensure proper backup procedures are in place to prevent data loss. Training in digital forensics equips officers with the skills needed to handle these complex cases effectively.
Emerging Technologies in Evidence Management

Emerging technologies are revolutionizing police evidence handling, making processes more efficient and reliable. Digital evidence management systems now allow law enforcement agencies to track, store, and retrieve evidence electronically. These systems reduce the risk of contamination or loss, ensuring the integrity of the evidence throughout the investigative process. According to a recent study by a leading forensic research institute, the adoption of digital evidence management systems has increased by 40% in the past five years.
Another significant advancement is the use of blockchain technology. This innovation creates an immutable record of evidence handling, providing a tamper-proof chain of custody. Every action taken with the evidence is recorded and verified, enhancing transparency and accountability. Police departments are increasingly integrating blockchain into their evidence management protocols to bolster the credibility of their investigations.
Additionally, artificial intelligence (AI) is playing a pivotal role. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of evidence quickly and accurately, identifying patterns and connections that might elude human investigators. This technology not only speeds up the investigative process but also improves the accuracy of the findings. As AI continues to evolve, its impact on police evidence handling is expected to grow exponentially.
Biometric technologies are also gaining traction. Fingerprint and DNA analysis have long been staples in forensic investigations, but newer biometric technologies, such as facial recognition and iris scanning, are becoming more prevalent. These technologies provide additional layers of verification, ensuring that evidence is handled and processed with the highest level of precision. The integration of these technologies into evidence management systems is a testament to the ongoing evolution of forensic science.
Proper police evidence handling is the backbone of any successful criminal investigation, ensuring the integrity and admissibility of crucial information. It involves a meticulous process from collection to presentation in court, safeguarding both the rights of the accused and the pursuit of justice. To uphold these standards, law enforcement agencies should regularly train personnel on the latest evidence handling protocols, emphasizing the importance of chain of custody and contamination prevention. As forensic technology evolves, so too must the methods and training programs designed to maintain the highest levels of evidence integrity, ensuring justice is served accurately and fairly.



