Police misconduct complaints in the U.S. have surged by 37% over the past decade, highlighting a critical need for effective oversight. Accountability in law enforcement isn’t just a bureaucratic concept—it’s a vital mechanism that ensures public safety and maintains community trust. When police officers are held accountable, it creates a system where justice is served, and communities feel protected rather than policed.
Understanding police accountability means grasping what is police accountability explained: a framework of policies, procedures, and oversight bodies that ensure officers act lawfully and ethically. What is police accountability explained also involves transparency, where departments disclose use-of-force incidents and disciplinary actions. This system isn’t just about punishing misconduct; it’s about preventing it through training, oversight, and clear consequences. For citizens, understanding these aspects means knowing their rights and how to seek recourse when those rights are violated.
The Foundation of Police Accountability
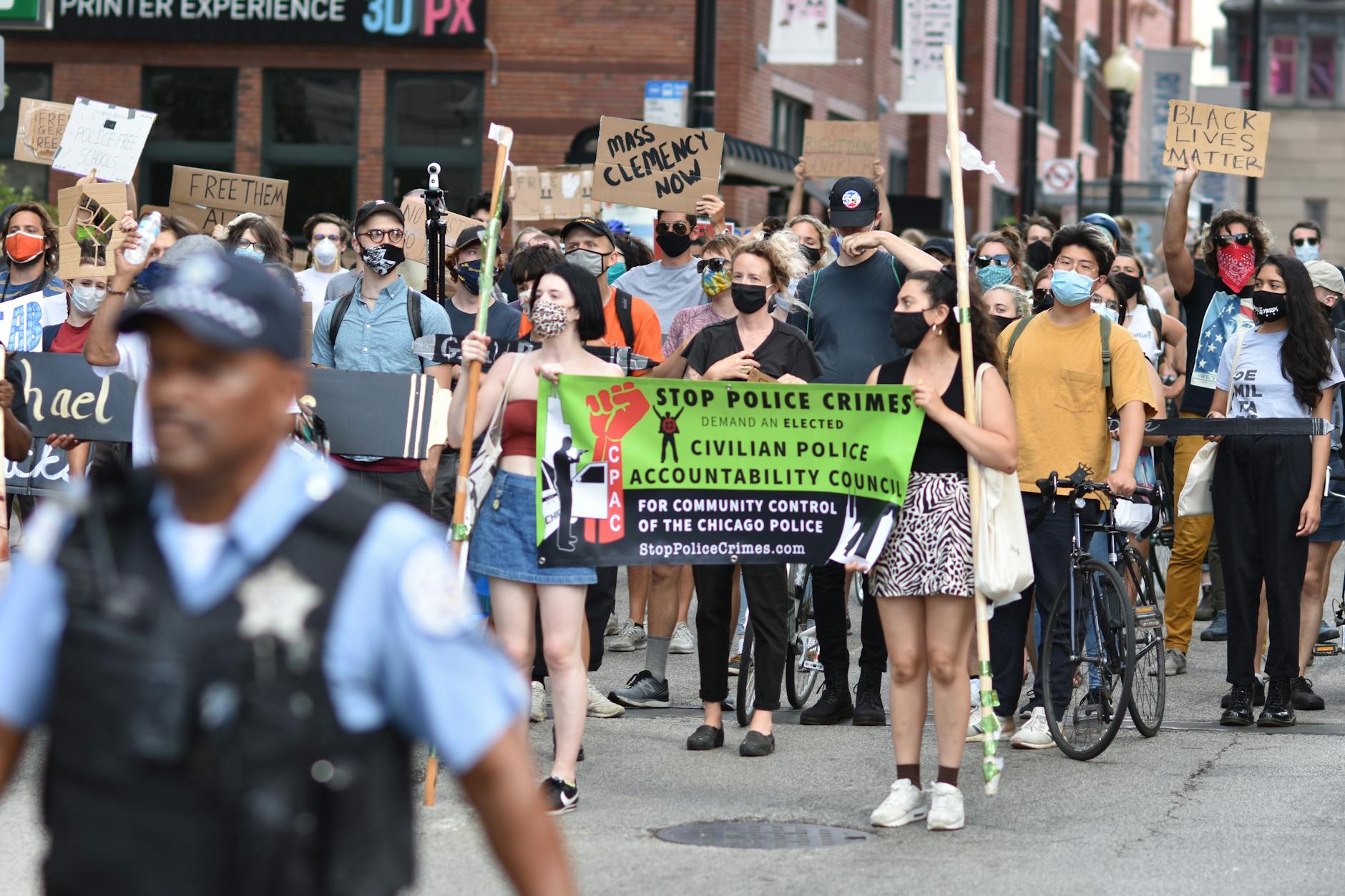
Police accountability refers to the mechanisms and processes that ensure law enforcement officers act within the bounds of the law and adhere to ethical standards. At its core, it’s about transparency, responsibility, and the public’s right to know how police forces operate. This foundation is built on several key principles, including clear policies, effective oversight, and consequences for misconduct.
A critical aspect of police accountability is the existence of clear, written policies that guide officers’ actions. These policies should be readily accessible to the public and regularly updated to reflect current best practices. According to a report by the Police Executive Research Forum, agencies with comprehensive use-of-force policies experience a 20% reduction in use-of-force incidents. This underscores the importance of having well-defined guidelines.
Oversight bodies, both internal and external, play a pivotal role in maintaining accountability. Internal affairs divisions investigate misconduct allegations, while civilian review boards provide an independent perspective. These entities ensure that complaints are thoroughly investigated and that appropriate disciplinary actions are taken when necessary. Their work is essential for building and maintaining public trust.
Consequences for misconduct are a cornerstone of police accountability. When officers violate policies or laws, they must face appropriate disciplinary measures. This can range from retraining to termination, depending on the severity of the offense. A study by the National Police Foundation found that departments with clear disciplinary processes have higher levels of officer compliance and public satisfaction. This highlights the importance of a fair and transparent disciplinary system.
Core Principles in Action
Police accountability operates through a framework of core principles designed to ensure transparency, fairness, and public trust. At its heart lies the concept of oversight, where independent bodies monitor police actions to prevent misconduct. These bodies, often civilian review boards or oversight commissions, investigate complaints and recommend disciplinary actions when necessary. Their role is crucial in maintaining a balance between police authority and public rights.
Another key principle is the use of technology. Body-worn cameras, for instance, have become a standard tool in many departments. A study by the Police Executive Research Forum found that agencies using body cameras saw a 50% reduction in citizen complaints. This technology provides objective evidence that can protect both officers and the public. It also serves as a deterrent for potential misconduct, fostering a culture of accountability within police ranks.
Clear policies and procedures also underpin police accountability. These guidelines outline expectations for officer conduct, use of force, and interactions with the public. Regular training ensures officers understand and adhere to these standards. Additionally, departments must have mechanisms for addressing policy violations promptly and fairly. This approach not only upholds accountability but also builds public confidence in the system.
Mechanisms Ensuring Responsibility

Police accountability relies on robust mechanisms that ensure officers act within legal and ethical boundaries. Internal affairs divisions serve as the first line of defense, investigating misconduct complaints and enforcing departmental policies. These units operate independently within police departments, providing a dedicated channel for addressing allegations of wrongdoing. Their existence underscores the commitment to maintaining high standards of professionalism among law enforcement officers.
A critical component of accountability is the civilian oversight board. Composed of community members, these boards review police conduct and make recommendations for policy changes. Their involvement fosters transparency and builds public trust. According to a recent study, departments with civilian oversight experience a 20% increase in public satisfaction with police conduct.
Technology also plays a pivotal role. Body-worn cameras and dashboard cameras provide objective evidence of interactions between officers and the public. These tools not only deter misconduct but also offer crucial documentation for investigations. Experts emphasize that the presence of cameras significantly improves the accuracy of incident reports and reduces disputes over what transpired during an encounter.
Additionally, regular training and evaluations ensure officers stay updated on best practices and legal standards. Mandatory training programs cover de-escalation techniques, cultural competency, and the use of force. Continuous education helps officers adapt to evolving community needs and legal requirements. This proactive approach demonstrates a commitment to ongoing improvement and accountability within the police force.
Community Involvement and Transparency

Police accountability hinges on community involvement and transparency. When law enforcement agencies operate openly, they foster trust and collaboration with the public they serve. This transparency can take many forms, from releasing body camera footage to publishing annual reports on use-of-force incidents. According to a recent study by the National Institute of Justice, communities where police departments maintain open lines of communication experience lower crime rates and higher public satisfaction.
Community involvement plays a crucial role in shaping police accountability. Citizens have the power to influence policy through participation in town halls, advisory boards, and public hearings. When residents engage with their local police departments, they help identify areas for improvement and advocate for reforms. This collaborative approach ensures that law enforcement strategies align with community values and priorities.
Transparency also extends to internal affairs investigations. Police departments must be forthcoming about misconduct allegations and the subsequent disciplinary actions. By doing so, they demonstrate their commitment to fairness and justice. However, achieving true transparency requires more than just releasing information—it demands a proactive effort to educate the public about the complexities of policing.
In some jurisdictions, independent oversight bodies have been established to enhance accountability. These entities, often composed of civilians, review complaints against police officers and make recommendations for reform. Their role is to provide an impartial perspective, free from the potential biases that can arise within police departments. By involving the community in these oversight efforts, police departments can build stronger, more trusting relationships with the people they serve.
Building a Future of Trust and Accountability

Police accountability represents a cornerstone of democratic governance, ensuring law enforcement agencies operate with transparency and respect for citizens’ rights. At its core, it involves mechanisms that monitor police conduct, investigate misconduct, and apply appropriate disciplinary measures. This system fosters public trust, as it demonstrates a commitment to justice and fairness. Without accountability, police forces risk becoming unchecked powers, potentially leading to abuses that erode community confidence.
A study by the National Institute of Justice reveals that 72% of Americans believe police accountability measures are crucial for maintaining public trust. These measures include independent oversight bodies, civilian review boards, and robust internal affairs divisions. Such structures provide avenues for citizens to report misconduct and seek redress. They also serve as deterrents, discouraging officers from engaging in unethical behavior.
Building a future of trust and accountability requires a multifaceted approach. It involves not only implementing strong policies but also fostering a culture of integrity within police departments. Training programs that emphasize de-escalation techniques and cultural sensitivity can significantly reduce incidents of misconduct. Additionally, promoting diversity within police ranks can enhance understanding and rapport with the communities they serve. Ultimately, accountability is not a one-time achievement but an ongoing process that demands continuous evaluation and improvement.
Police accountability is the cornerstone of public trust in law enforcement, ensuring officers act within the bounds of the law and uphold community values. It encompasses transparency, oversight, and consequences for misconduct, all of which are vital for maintaining justice and fairness. To foster accountability, communities should actively engage with local police departments, advocating for clear policies, independent oversight, and accessible complaint processes. As society evolves, so too must the mechanisms of police accountability, requiring ongoing dialogue and reform to better serve and protect all citizens.



